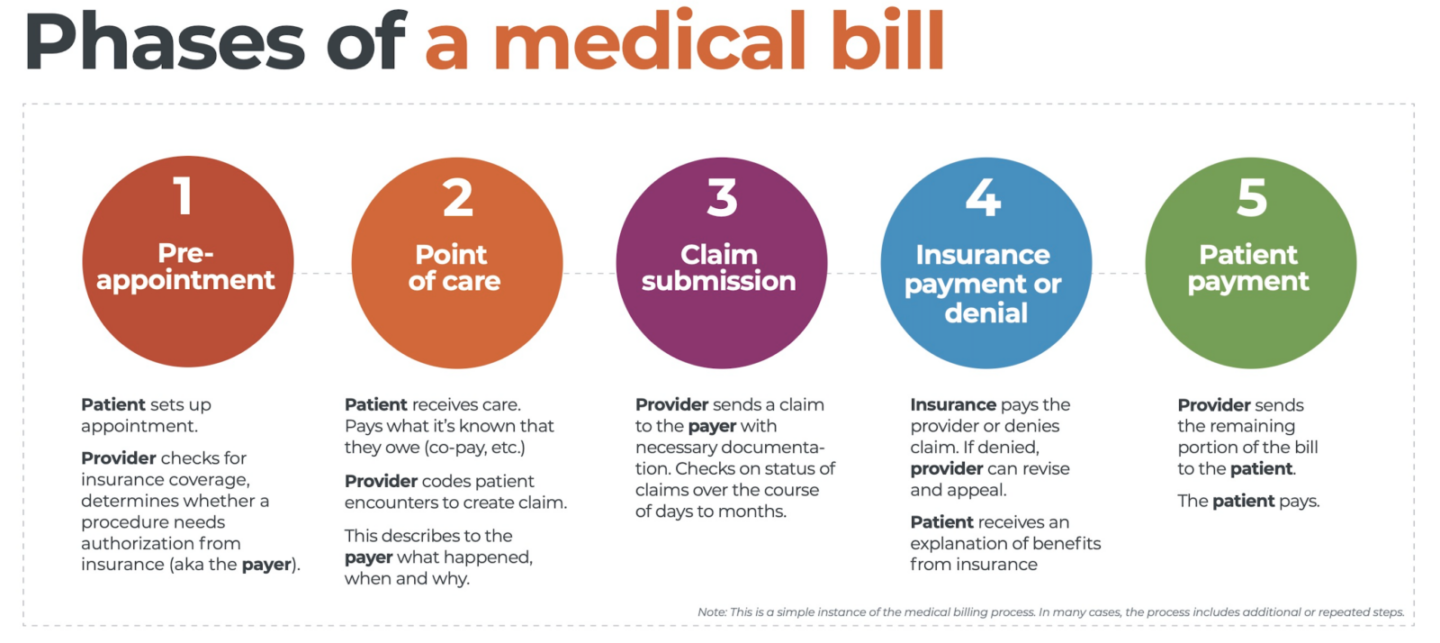
1. What is Health Insurance?
Health insurance is a contract between you and an insurance company. You pay a monthly premium, and in return, the insurance provider helps cover medical costs, including doctor visits, hospital stays, medications, and preventive care.
2. Key Terms to Know
- Premium: The amount you pay monthly or annually for your health insurance plan.
- Deductible: The amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance starts covering costs.
- Copayment (Copay): A fixed amount you pay for certain services, like doctor visits or prescriptions.
- Coinsurance: The percentage of medical costs you pay after meeting your deductible.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The most you will pay in a year before your insurance covers 100% of eligible expenses.
- Network: A group of doctors, hospitals, and healthcare providers that have agreed to offer services at reduced rates to plan members.
3. Types of Health Insurance Plans
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): Requires you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and get referrals to see specialists. It offers lower costs but less flexibility.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): Offers more flexibility to see any doctor or specialist without referrals, but costs may be higher.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): Covers only in-network providers except in emergencies.
- Point of Service (POS): A hybrid of HMO and PPO, requiring referrals for specialists but allowing out-of-network care at a higher cost.
- High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): Has lower premiums but higher deductibles, often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA) to save for medical expenses tax-free.
4. Why is Health Insurance Important?
- Financial Protection: Covers major medical expenses that could otherwise lead to debt.
- Preventive Care: Encourages regular check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings.
- Access to Better Healthcare: Ensures you can see specialists and receive necessary treatments without delay.
- Legal Requirement: In some countries, having health insurance is mandatory to avoid penalties.
5. How to Choose the Right Plan
- Assess Your Needs: Consider how often you visit doctors, your prescription needs, and any ongoing medical conditions.
- Compare Costs: Look at premiums, deductibles, copays, and out-of-pocket maximums.
- Check Provider Networks: Ensure your preferred doctors and hospitals are included.
- Understand Coverage: Review what services, medications, and treatments are covered.
- Look for Additional Benefits: Some plans include wellness programs, mental health coverage, and telemedicine services.
6. How to Use Your Health Insurance
- Find an In-Network Doctor: This helps reduce costs.
- Schedule Preventive Care: Many plans cover screenings and vaccinations at no extra cost.
- Understand Your Bills: Know what portion of your medical expenses you are responsible for.
- Use Telemedicine: Many plans offer virtual doctor visits for minor health issues.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Not Understanding the Plan: Read the terms carefully to know what’s covered and what’s not.
- Choosing the Cheapest Plan Without Considering Coverage: Low premiums may mean high out-of-pocket costs.
- Ignoring Preventive Care: Regular check-ups can prevent costly medical issues later.
- Missing Enrollment Deadlines: Sign up during open enrollment to avoid gaps in coverage.
Conclusion
Health insurance is an essential part of financial and medical well-being. Understanding its basics—key terms, plan types, costs, and benefits—can help you make informed decisions and get the most out of your coverage. Whether you’re choosing a plan for the first time or looking to optimize your current one, being informed ensures you receive quality care without unnecessary financial strain.


